Powell Addresses Interest Rates, Inflation, and Economic Challenges
Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell delivered a highly anticipated speech to the Economic Club of New York, addressing key issues related to interest rates and inflation. In his speech, Powell emphasized the Federal Reserve’s resolute commitment to its 2% mandate regarding inflation, shedding light on the future direction of U.S. monetary policy.
Market Reaction
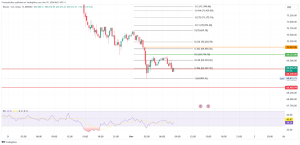
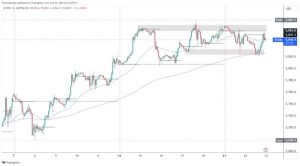
As Powell addressed the audience, it became clear that futures market traders shouldn’t wait for a rate hike in November. Moreover, there’s a small chance of a such move even in December. However, Powell acknowledged the progress made toward controlling inflation, following a series of interest rate hikes aimed at mitigating its impact.
Powell’s Perspective on Rates
When asked about the current interest rates, the Fed Chairman indicated that, in his view, policy wasn’t excessively tight. However, he acknowledged the challenges associated with higher interest rates. According to Powell, the latter can be difficult for everyone. He also highlighted the complexities of managing interest rates and inflation.
Progress in Taming Inflation
Powell noted the progress made in achieving the Federal Reserve’s dual mandate goals of maximum employment and stable prices, primarily dealing with the issue of inflation. Recent data showed a slowing pace of inflation, although it remained above the target rate. The annual rate had decreased to 3.7% from over 9% in June 2022. It reflected the ongoing efforts to control the effects of inflation.
Challenges Ahead
Powell’s speech faced an initial disruption from Climate Defiance protesters. However, he continued to address not only inflation risk but also the need for a period of below-trend economic growth. The Fed official also discussed further softening in labor market conditions. The Federal Reserve has raised interest rates 11 times since March 2022, a total of 5.25 percentage points. The agency hoped to counter the challenges posed by interest rates and inflation.
Economic Outlook
On the same day, initial jobless claims reached their lowest weekly level since early 2023, indicating a tight labor market that could exert upward pressure on inflation bounce. Powell cautioned that the emergence of continued above-trend growth or a labor market no longer easing might jeopardize further progress on inflation. It might also potentially necessitate additional tightening of monetary policy. This underscored the enduring complexities involved in managing interest rates and inflation.